How Many Data Records Are Read During Data Step Execution?
Chances are, if yous teach the master grades, you have to do running records. But what are running records, and how do they help you teach reading? Never fear, WeAreTeachers is here to explain it all.
What are running records?
Running records fall under the reading assessments portion of your readers' workshop. They're part read aloud cess (think: fluency cess) and part observation. The goal of a running tape is, first, to run into how the pupil is using the strategies you're educational activity in class, and second, to find out if the student is ready to advance in a reading-level system if your school uses one (Reading A to Z, Fountas and Pinnell, and others). Thinking about educational activity, when you combine a running record with some analysis, you can address student mistakes and plan their next steps.
When do I utilize running records?
Running records are used to collect information on young readers who are still reading aloud and working on basic skills (think: those who are at reading levels aa–J). A running record captures both how well a pupil reads (the number of words they read correctly) and their reading behaviors (what they say and practise as they read). At the start of the year, or when you showtime working with a educatee, a running record can help match the pupil with books that are correct for them. And then, yous can employ subsequent running records to track the student'due south progress.
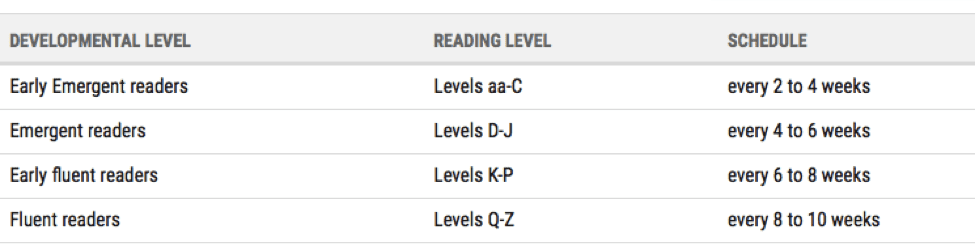
Once you practise the first running record, the time in betwixt running records will depend on how well the child is progressing and what level they are reading. An emergent reader (using Reading A to Z levels aa–C, for example) will be assessed every two to iv weeks, while a fluent reader (level Q–Z) should exist assessed every 8 to 10 weeks. Essentially, students who are learning the fundamentals are assessed more often than students who are working on fluency and higher-club comprehension.
Here'south a sample running records assessment schedule from Learning A–Z.
Why do I practise running records?
Proficient readers use what is happening in the text (meaning), knowledge of language and grammar (structural), and visual cues (words and discussion parts) to read. Beginning readers are learning how to practice this, and then running records provide a fashion to detect how they are approaching text.
For whatever text that a child reads, running records aid you lot answer these questions:
- What is the child's word reading and fluency? Or, tin can they read smoothly and accurately? (Get our free fluency posters hither.)
- Are they able to self-monitor and correct their mistakes while reading?
- Are they able to use meaning, construction, and visual cues to understand what they read?
- What do they do when they come up across a word they don't know? (Cheque out our list of vocabulary games.)
- Are they using strategies that y'all taught in class?
- How are they improving in their reading over time?
How practice I do a running record?
Every running record follows the same procedure:
- Sit down next to the child and so yous tin can follow along with them as they read.
- Choose a passage or volume that is at the educatee's approximate reading level. (If you lot're wrong on the level, you can conform upwardly or down to get the correct fit. If you're not focusing on level, cull something that the child is working on in class.)
- Tell the kid that they will read out loud every bit you listen and jot some notes nearly their reading.
- Equally the kid reads, go along a record past using a running record form (a typed paper of the aforementioned passage the student is reading). Mark the page past putting a checkmark higher up each word that is read correctly and marking errors. Hither is an overview of how to mark miscues in a running tape.
- While the pupil is reading, intervene as little as possible.
- Lookout man for how the educatee is using the strategies that you taught in class and pay attention to how the student is gathering meaning using structural, meaning, or visual cues.
- If the educatee gets stuck on the give-and-take, wait five seconds then tell them the word. If the student is dislocated, explain the word and tell them to try again.
- Afterward the student reads the passage, inquire them to retell what they read. Or, ask a few basic comprehension questions: Who was in the story? Where did the story take identify? What happened?
- After the running record, briefing with the student to provide praise (for self-correcting or using reading strategies) and effective feedback (review errors and have them reread portions correctly).
Okay, I did the running record, now what?
Yay! You have all the data! Now it'south time to analyze information technology.
Calculate the accuracy: (number of words in the passage – number of uncorrected mistakes) 10 100 / number of words in the passage. For case: (218 words – 9 errors) x 100 / 218 = 96%.
Use the student'southward accuracy charge per unit to put them in a reading level. As a general dominion of thumb, if a child can read 95–100 per centum of the words in a text correctly, they tin read independently. When they are reading 90–94 percentage of words correctly, they are reading at instructional level and will need teacher support. If a kid is reading less than 89 percent of the words correctly, it'due south likely they're not reading enough words to understand the text fully.
If students are reading at an independent level (95 pct accuracy and higher) and have strong comprehension (they have a strong retelling or answer 100 percent of the comprehension questions correctly), so they are ready to advance to some other reading level.
Use this running records tip sheet for more information on how to use running record data to plan education.
This sounds similar a lot of work. How exercise I proceed it organized?
- Create a schedule for assessing students. Assign each student a day of the calendar week or month to brand certain each student has a running record that is updated regularly.
- Go along a data notebook with a department for each student that includes their running record. A running record should show that students are reading at a higher level, and with increased accurateness.
- Set a goal with students. Set up an almanac goal around the reading behavior they want to strengthen, the level that they need to be reading on, or the number of levels they would like to advance. At each conference, talk about how they are progressing toward the goal and what they can practise to improve between running records.
Get more resources on running records:
- Watch a running record to get an idea of how one instructor implements it.
- Information near reading fluency and how to support it in the classroom
- Teacher hacks to make data collection easy
Ask questions and share your advice for running records in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.

How Many Data Records Are Read During Data Step Execution?,
Source: https://www.weareteachers.com/what-are-running-records/
Posted by: fischerlableason.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Many Data Records Are Read During Data Step Execution?"
Post a Comment